Instructions
Markup
Here’s a barebones example of a fully working reveal.js presentation:
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/reveal.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/theme/white.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="reveal">
<div class="slides">
<section>Slide 1</section>
<section>Slide 2</section>
</div>
</div>
<script src="js/reveal.js"></script>
<script>
Reveal.initialize();
</script>
</body>
</html>The presentation markup hierarchy needs to be .reveal > .slides > section where the section represents one slide and can be repeated indefinitely. If you place multiple section elements inside of another section they will be shown as vertical slides. The first of the vertical slides is the “root” of the others (at the top), and will be included in the horizontal sequence. For example:
<div class="reveal">
<div class="slides">
<section>Single Horizontal Slide</section>
<section>
<section>Vertical Slide 1</section>
<section>Vertical Slide 2</section>
</section>
</div>
</div>Markdown
It’s possible to write your slides using Markdown. To enable Markdown, add the data-markdown attribute to your <section> elements and wrap the contents in a <textarea data-template> like the example below. You’ll also need to add the plugin/markdown/marked.js and plugin/markdown/markdown.js scripts (in that order) to your HTML file.
This is based on data-markdown from Paul Irish modified to use marked to support GitHub Flavored Markdown. Sensitive to indentation (avoid mixing tabs and spaces) and line breaks (avoid consecutive breaks).
<section data-markdown>
<textarea data-template>
## Page title
A paragraph with some text and a [link](http://hakim.se).
</textarea>
</section>External Markdown
You can write your content as a separate file and have reveal.js load it at runtime. Note the separator arguments which determine how slides are delimited in the external file: the data-separator attribute defines a regular expression for horizontal slides (defaults to ^\r?\n---\r?\n$, a newline-bounded horizontal rule) and data-separator-vertical defines vertical slides (disabled by default). The data-separator-notes attribute is a regular expression for specifying the beginning of the current slide’s speaker notes (defaults to notes?:, so it will match both “note:” and “notes:“). The data-charset attribute is optional and specifies which charset to use when loading the external file.
When used locally, this feature requires that reveal.js runs from a local web server. The following example customises all available options:
<section data-markdown="example.md"
data-separator="^\n\n\n"
data-separator-vertical="^\n\n"
data-separator-notes="^Note:"
data-charset="iso-8859-15">
<!--
Note that Windows uses `\r\n` instead of `\n` as its linefeed character.
For a regex that supports all operating systems, use `\r?\n` instead of `\n`.
-->
</section>Element Attributes
Special syntax (through HTML comments) is available for adding attributes to Markdown elements. This is useful for fragments, amongst other things.
<section data-markdown>
<script type="text/template">
- Item 1 <!-- .element: class="fragment" data-fragment-index="2" -->
- Item 2 <!-- .element: class="fragment" data-fragment-index="1" -->
</script>
</section>Slide Attributes
Special syntax (through HTML comments) is available for adding attributes to the slide <section> elements generated by your Markdown.
<section data-markdown>
<script type="text/template">
<!-- .slide: data-background="#ff0000" -->
Markdown content
</script>
</section>Configuring marked
We use marked to parse Markdown. To customise marked’s rendering, you can pass in options when configuring Reveal:
Reveal.initialize({
// Options which are passed into marked
// See https://marked.js.org/#/USING_ADVANCED.md#options
markdown: {
smartypants: true
}
});
Configuration
At the end of your page you need to initialize reveal by running the following code. Note that all configuration values are optional and will default to the values specified below.
Reveal.initialize({
// Display presentation control arrows
controls: true,
// Help the user learn the controls by providing hints, for example by
// bouncing the down arrow when they first encounter a vertical slide
controlsTutorial: true,
// Determines where controls appear, "edges" or "bottom-right"
controlsLayout: 'bottom-right',
// Visibility rule for backwards navigation arrows; "faded", "hidden"
// or "visible"
controlsBackArrows: 'faded',
// Display a presentation progress bar
progress: true,
// Display the page number of the current slide
slideNumber: false,
// Add the current slide number to the URL hash so that reloading the
// page/copying the URL will return you to the same slide
hash: false,
// Push each slide change to the browser history. Implies `hash: true`
history: false,
// Enable keyboard shortcuts for navigation
keyboard: true,
// Enable the slide overview mode
overview: true,
// Vertical centering of slides
center: true,
// Enables touch navigation on devices with touch input
touch: true,
// Loop the presentation
loop: false,
// Change the presentation direction to be RTL
rtl: false,
// See https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js/#navigation-mode
navigationMode: 'default',
// Randomizes the order of slides each time the presentation loads
shuffle: false,
// Turns fragments on and off globally
fragments: true,
// Flags whether to include the current fragment in the URL,
// so that reloading brings you to the same fragment position
fragmentInURL: false,
// Flags if the presentation is running in an embedded mode,
// i.e. contained within a limited portion of the screen
embedded: false,
// Flags if we should show a help overlay when the questionmark
// key is pressed
help: true,
// Flags if speaker notes should be visible to all viewers
showNotes: false,
// Global override for autoplaying embedded media (video/audio/iframe)
// - null: Media will only autoplay if data-autoplay is present
// - true: All media will autoplay, regardless of individual setting
// - false: No media will autoplay, regardless of individual setting
autoPlayMedia: null,
// Global override for preloading lazy-loaded iframes
// - null: Iframes with data-src AND data-preload will be loaded when within
// the viewDistance, iframes with only data-src will be loaded when visible
// - true: All iframes with data-src will be loaded when within the viewDistance
// - false: All iframes with data-src will be loaded only when visible
preloadIframes: null,
// Number of milliseconds between automatically proceeding to the
// next slide, disabled when set to 0, this value can be overwritten
// by using a data-autoslide attribute on your slides
autoSlide: 0,
// Stop auto-sliding after user input
autoSlideStoppable: true,
// Use this method for navigation when auto-sliding
autoSlideMethod: Reveal.navigateNext,
// Specify the average time in seconds that you think you will spend
// presenting each slide. This is used to show a pacing timer in the
// speaker view
defaultTiming: 120,
// Enable slide navigation via mouse wheel
mouseWheel: false,
// Hide cursor if inactive
hideInactiveCursor: true,
// Time before the cursor is hidden (in ms)
hideCursorTime: 5000,
// Hides the address bar on mobile devices
hideAddressBar: true,
// Opens links in an iframe preview overlay
// Add `data-preview-link` and `data-preview-link="false"` to customise each link
// individually
previewLinks: false,
// Transition style
transition: 'slide', // none/fade/slide/convex/concave/zoom
// Transition speed
transitionSpeed: 'default', // default/fast/slow
// Transition style for full page slide backgrounds
backgroundTransition: 'fade', // none/fade/slide/convex/concave/zoom
// Number of slides away from the current that are visible
viewDistance: 3,
// Parallax background image
parallaxBackgroundImage: '', // e.g. "'https://s3.amazonaws.com/hakim-static/reveal-js/reveal-parallax-1.jpg'"
// Parallax background size
parallaxBackgroundSize: '', // CSS syntax, e.g. "2100px 900px"
// Number of pixels to move the parallax background per slide
// - Calculated automatically unless specified
// - Set to 0 to disable movement along an axis
parallaxBackgroundHorizontal: null,
parallaxBackgroundVertical: null,
// The display mode that will be used to show slides
display: 'block'
});
The configuration can be updated after initialization using the configure method:
// Turn autoSlide off
Reveal.configure({ autoSlide: 0 });
// Start auto-sliding every 5s
Reveal.configure({ autoSlide: 5000 });
Presentation Size
All presentations have a normal size, that is, the resolution at which they are authored. The framework will automatically scale presentations uniformly based on this size to ensure that everything fits on any given display or viewport.
See below for a list of configuration options related to sizing, including default values:
Reveal.initialize({
// ...
// The "normal" size of the presentation, aspect ratio will be preserved
// when the presentation is scaled to fit different resolutions. Can be
// specified using percentage units.
width: 960,
height: 700,
// Factor of the display size that should remain empty around the content
margin: 0.1,
// Bounds for smallest/largest possible scale to apply to content
minScale: 0.2,
maxScale: 1.5
});
If you wish to disable this behavior and do your own scaling (e.g. using media queries), try these settings:
Reveal.initialize({
// ...
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
margin: 0,
minScale: 1,
maxScale: 1
});
Dependencies
Reveal.js doesn’t rely on any third party scripts to work but a few optional libraries are included by default. These libraries are loaded as dependencies in the order they appear, for example:
Reveal.initialize({
dependencies: [
// Interpret Markdown in <section> elements
{ src: 'plugin/markdown/marked.js', condition: function() { return !!document.querySelector( '[data-markdown]' ); } },
{ src: 'plugin/markdown/markdown.js', condition: function() { return !!document.querySelector( '[data-markdown]' ); } },
// Syntax highlight for <code> elements
{ src: 'plugin/highlight/highlight.js', async: true },
// Zoom in and out with Alt+click
{ src: 'plugin/zoom-js/zoom.js', async: true },
// Speaker notes
{ src: 'plugin/notes/notes.js', async: true },
// MathJax
{ src: 'plugin/math/math.js', async: true }
]
});
You can add your own extensions using the same syntax. The following properties are available for each dependency object: - src: Path to the script to load - async: [optional] Flags if the script should load after reveal.js has started, defaults to false - callback: [optional] Function to execute when the script has loaded - condition: [optional] Function which must return true for the script to be loaded
Ready Event
A ready event is fired when reveal.js has loaded all non-async dependencies and is ready to start navigating. To check if reveal.js is already ‘ready’ you can call Reveal.isReady().
Reveal.addEventListener( 'ready', function( event ) {
// event.currentSlide, event.indexh, event.indexv
} );
Note that we also add a .ready class to the .reveal element so that you can hook into this with CSS.
Auto-sliding
Presentations can be configured to progress through slides automatically, without any user input. To enable this you will need to tell the framework how many milliseconds it should wait between slides:
// Slide every five seconds
Reveal.configure({
autoSlide: 5000
});
When this is turned on a control element will appear that enables users to pause and resume auto-sliding. Alternatively, sliding can be paused or resumed by pressing »A« on the keyboard. Sliding is paused automatically as soon as the user starts navigating. You can disable these controls by specifying autoSlideStoppable: false in your reveal.js config.
You can also override the slide duration for individual slides and fragments by using the data-autoslide attribute:
<section data-autoslide="2000">
<p>After 2 seconds the first fragment will be shown.</p>
<p class="fragment" data-autoslide="10000">After 10 seconds the next fragment will be shown.</p>
<p class="fragment">Now, the fragment is displayed for 2 seconds before the next slide is shown.</p>
</section>To override the method used for navigation when auto-sliding, you can specify the autoSlideMethod setting. To only navigate along the top layer and ignore vertical slides, set this to Reveal.navigateRight.
Whenever the auto-slide mode is resumed or paused the autoslideresumed and autoslidepaused events are fired.
Keyboard Bindings
If you’re unhappy with any of the default keyboard bindings you can override them using the keyboard config option:
Reveal.configure({
keyboard: {
13: 'next', // go to the next slide when the ENTER key is pressed
27: function() {}, // do something custom when ESC is pressed
32: null // don't do anything when SPACE is pressed (i.e. disable a reveal.js default binding)
}
});
Vertical Slide Navigation
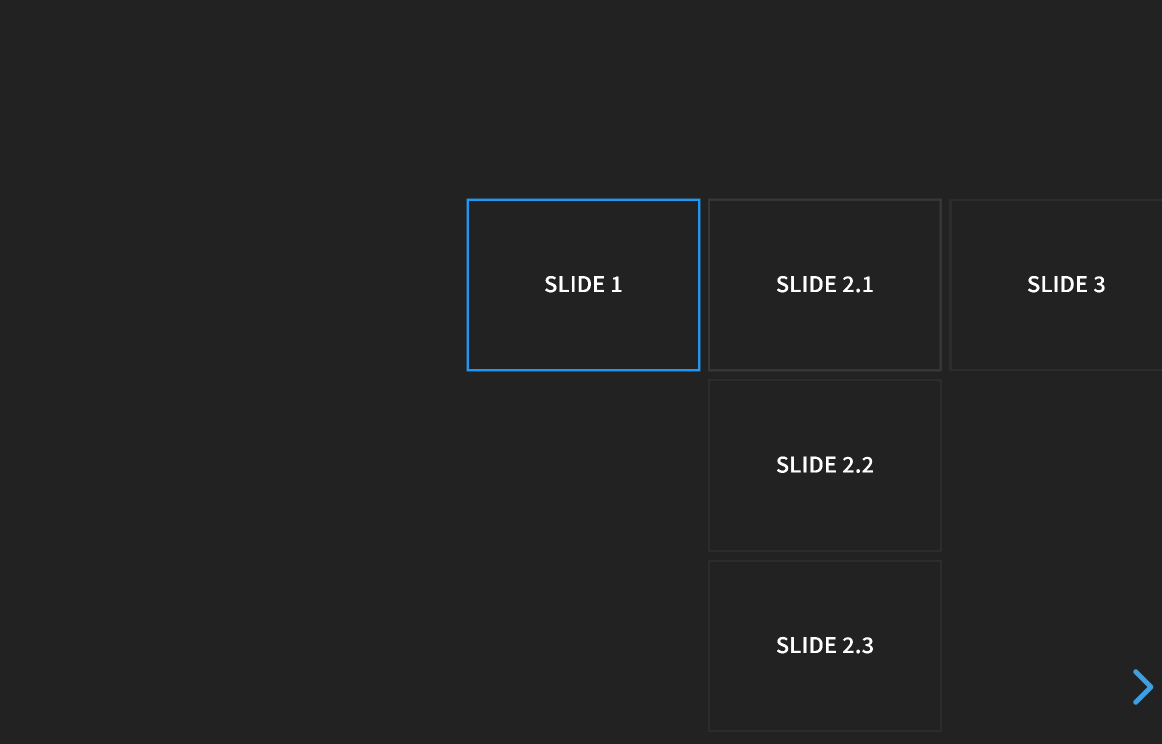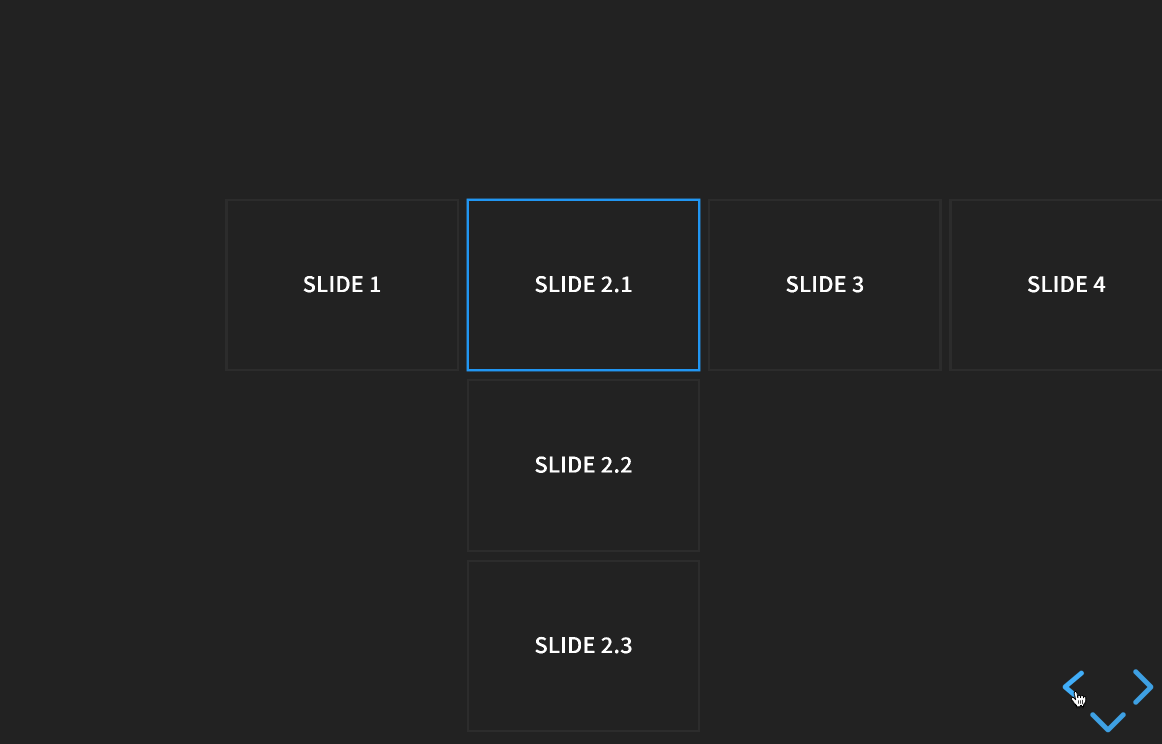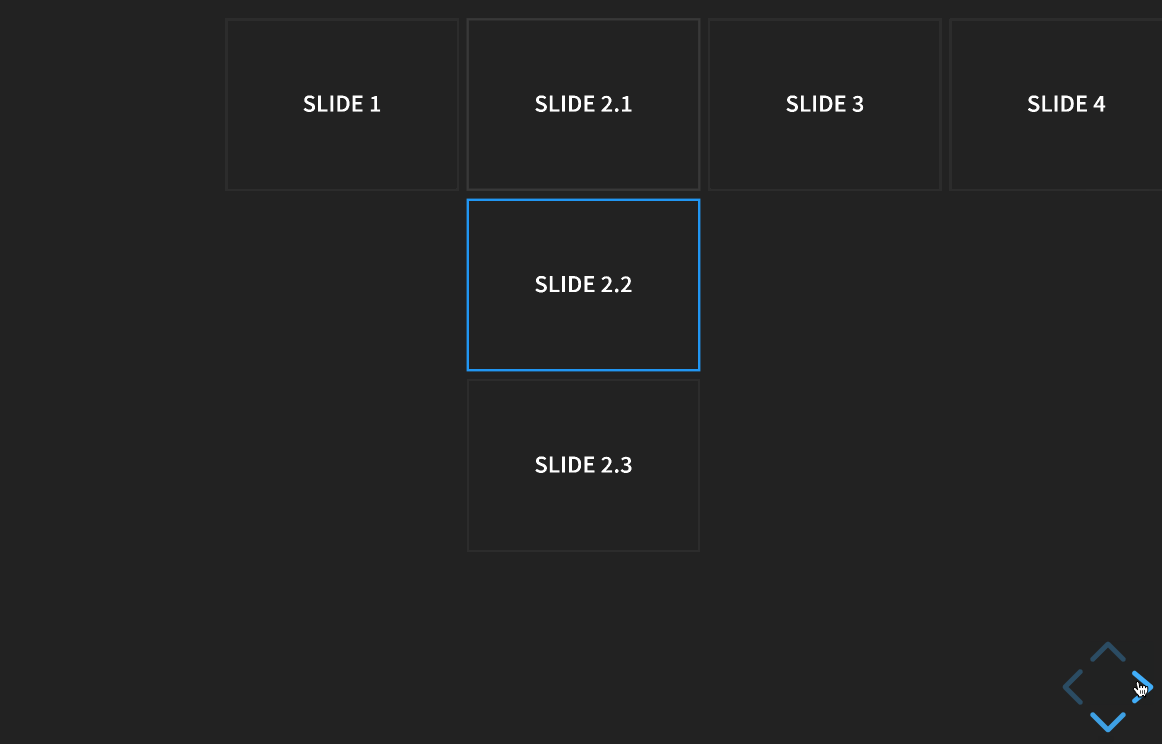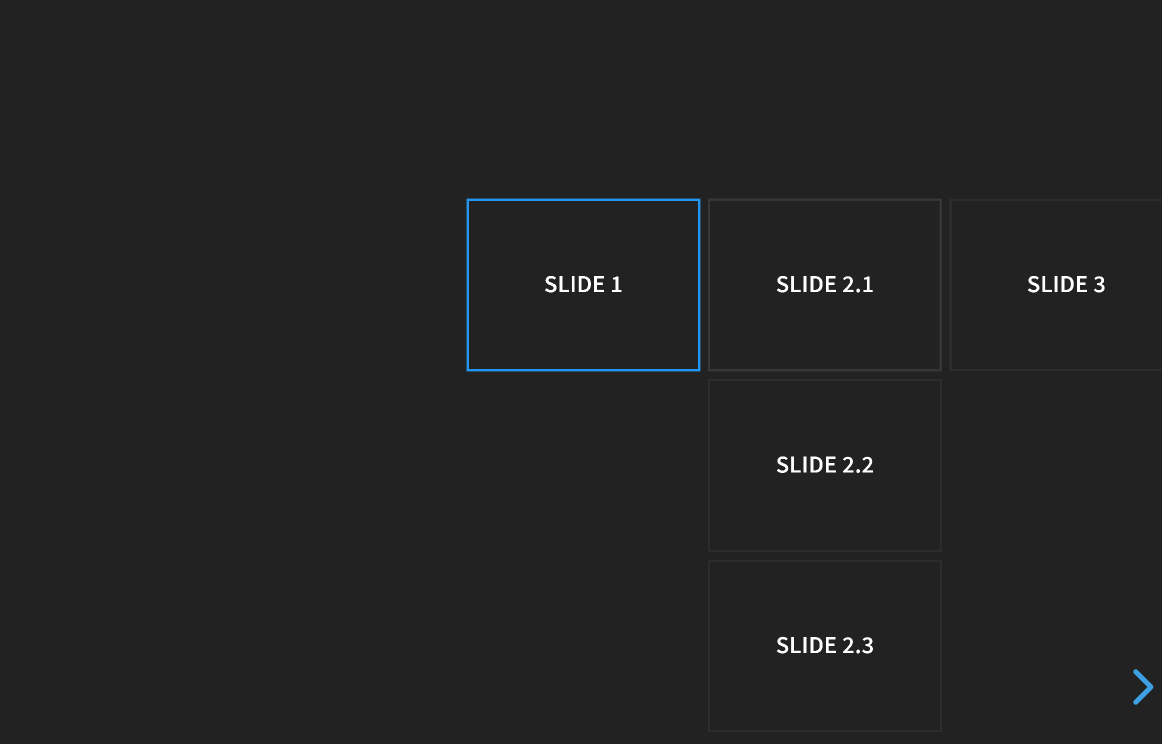
Slides can be nested within other slides to create vertical stacks (see Markup). When presenting, you use the left/right arrows to step through the main (horizontal) slides. When you arrive at a vertical stack you can optionally press the up/down arrows to view the vertical slides or skip past them by pressing the right arrow. Here’s an example showing a bird’s-eye view of what this looks like in action:
Navigation Mode
You can finetune the reveal.js navigation behavior by using the navigationMode config option. Note that these options are only useful for presnetations that use a mix of horizontal and vertical slides. The following navigation modes are available:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| default | Left/right arrow keys step between horizontal slides. Up/down arrow keys step between vertical slides. Space key steps through all slides (both horizontal and vertical). |
| linear | Removes the up/down arrows. Left/right arrows step through all slides (both horizontal and vertical). |
| grid | When this is enabled, stepping left/right from a vertical stack to an adjacent vertical stack will land you at the same vertical index. Consider a deck with six slides ordered in two vertical stacks: 1.1 2.11.2 2.21.3 2.3If you’re on slide 1.3 and navigate right, you will normally move from 1.3 -> 2.1. With navigationMode set to “grid” the same navigation takes you from 1.3 -> 2.3. |
Touch Navigation
You can swipe to navigate through a presentation on any touch-enabled device. Horizontal swipes change between horizontal slides, vertical swipes change between vertical slides. If you wish to disable this you can set the touch config option to false when initializing reveal.js.
If there’s some part of your content that needs to remain accessible to touch events you’ll need to highlight this by adding a data-prevent-swipe attribute to the element. One common example where this is useful is elements that need to be scrolled.
Lazy Loading
When working on presentation with a lot of media or iframe content it’s important to load lazily. Lazy loading means that reveal.js will only load content for the few slides nearest to the current slide. The number of slides that are preloaded is determined by the viewDistance configuration option.
To enable lazy loading all you need to do is change your src attributes to data-src as shown below. This is supported for image, video, audio and iframe elements.
<section>
<img data-src="image.png">
<iframe data-src="http://hakim.se"></iframe>
<video>
<source data-src="video.webm" type="video/webm" />
<source data-src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4" />
</video>
</section>Lazy Loading Iframes
Note that lazy loaded iframes ignore the viewDistance configuration and will only load when their containing slide becomes visible. Iframes are also unloaded as soon as the slide is hidden.
When we lazy load a video or audio element, reveal.js won’t start playing that content until the slide becomes visible. However there is no way to control this for an iframe since that could contain any kind of content. That means if we loaded an iframe before the slide is visible on screen it could begin playing media and sound in the background.
You can override this behavior with the data-preload attribute. The iframe below will be loaded
according to the viewDistance.
<section>
<iframe data-src="http://hakim.se" data-preload></iframe>
</section>You can also change the default globally with the preloadIframes configuration option. If set to
true ALL iframes with a data-src attribute will be preloaded when within the viewDistance
regardless of individual data-preload attributes. If set to false, all iframes will only be
loaded when they become visible.
API
The Reveal object exposes a JavaScript API for controlling navigation and reading state:
// Navigation
Reveal.slide( indexh, indexv, indexf );
Reveal.left();
Reveal.right();
Reveal.up();
Reveal.down();
Reveal.prev();
Reveal.next();
Reveal.prevFragment();
Reveal.nextFragment();
// Randomize the order of slides
Reveal.shuffle();
// Toggle presentation states, optionally pass true/false to force on/off
Reveal.toggleOverview();
Reveal.togglePause();
Reveal.toggleAutoSlide();
// Shows a help overlay with keyboard shortcuts, optionally pass true/false
// to force on/off
Reveal.toggleHelp();
// Change a config value at runtime
Reveal.configure({ controls: true });
// Returns the present configuration options
Reveal.getConfig();
// Fetch the current scale of the presentation
Reveal.getScale();
// Retrieves the previous and current slide elements
Reveal.getPreviousSlide();
Reveal.getCurrentSlide();
Reveal.getIndices(); // { h: 0, v: 0, f: 0 }
Reveal.getSlidePastCount();
Reveal.getProgress(); // (0 == first slide, 1 == last slide)
Reveal.getSlides(); // Array of all slides
Reveal.getTotalSlides(); // Total number of slides
// Returns the speaker notes for the current slide
Reveal.getSlideNotes();
// State checks
Reveal.isFirstSlide();
Reveal.isLastSlide();
Reveal.isOverview();
Reveal.isPaused();
Reveal.isAutoSliding();
// Returns the top-level DOM element
getRevealElement(); // <div class="reveal">...</div>
Custom Key Bindings
Custom key bindings can be added and removed using the following Javascript API. Custom key bindings will override the default keyboard bindings, but will in turn be overridden by the user defined bindings in the keyboard config option.
Reveal.addKeyBinding( binding, callback );
Reveal.removeKeyBinding( keyCode );
For example
// The binding parameter provides the following properties
// keyCode: the keycode for binding to the callback
// key: the key label to show in the help overlay
// description: the description of the action to show in the help overlay
Reveal.addKeyBinding( { keyCode: 84, key: 'T', description: 'Start timer' }, function() {
// start timer
} )
// The binding parameter can also be a direct keycode without providing the help description
Reveal.addKeyBinding( 82, function() {
// reset timer
} )
This allows plugins to add key bindings directly to Reveal so they can
- make use of Reveal’s pre-processing logic for key handling (for example, ignoring key presses when paused); and
- be included in the help overlay (optional)
Slide Changed Event
A slidechanged event is fired each time the slide is changed (regardless of state). The event object holds the index values of the current slide as well as a reference to the previous and current slide HTML nodes.
Some libraries, like MathJax (see #226), get confused by the transforms and display states of slides. Often times, this can be fixed by calling their update or render function from this callback.
Reveal.addEventListener( 'slidechanged', function( event ) {
// event.previousSlide, event.currentSlide, event.indexh, event.indexv
} );
Presentation State
The presentation’s current state can be fetched by using the getState method. A state object contains all of the information required to put the presentation back as it was when getState was first called. Sort of like a snapshot. It’s a simple object that can easily be stringified and persisted or sent over the wire.
Reveal.slide( 1 );
// we're on slide 1
var state = Reveal.getState();
Reveal.slide( 3 );
// we're on slide 3
Reveal.setState( state );
// we're back on slide 1
Slide States
If you set data-state="somestate" on a slide <section>, “somestate” will be applied as a class on the document element when that slide is opened. This allows you to apply broad style changes to the page based on the active slide.
Furthermore you can also listen to these changes in state via JavaScript:
Reveal.addEventListener( 'somestate', function() {
// TODO: Sprinkle magic
}, false );
Slide Backgrounds
Slides are contained within a limited portion of the screen by default to allow them to fit any display and scale uniformly. You can apply full page backgrounds outside of the slide area by adding a data-background attribute to your <section> elements. Four different types of backgrounds are supported: color, image, video and iframe.
Color Backgrounds
All CSS color formats are supported, including hex values, keywords, rgba() or hsl().
<section data-background-color="#ff0000">
<h2>Color</h2>
</section>Image Backgrounds
By default, background images are resized to cover the full page. Available options:
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data-background-image | URL of the image to show. GIFs restart when the slide opens. | |
| data-background-size | cover | See background-size on MDN. |
| data-background-position | center | See background-position on MDN. |
| data-background-repeat | no-repeat | See background-repeat on MDN. |
| data-background-opacity | 1 | Opacity of the background image on a 0-1 scale. 0 is transparent and 1 is fully opaque. |
<section data-background-image="http://example.com/image.png">
<h2>Image</h2>
</section>
<section data-background-image="http://example.com/image.png" data-background-size="100px" data-background-repeat="repeat">
<h2>This background image will be sized to 100px and repeated</h2>
</section>Video Backgrounds
Automatically plays a full size video behind the slide.
| Attribute | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| data-background-video | A single video source, or a comma separated list of video sources. | |
| data-background-video-loop | false | Flags if the video should play repeatedly. |
| data-background-video-muted | false | Flags if the audio should be muted. |
| data-background-size | cover | Use cover for full screen and some cropping or contain for letterboxing. |
| data-background-opacity | 1 | Opacity of the background video on a 0-1 scale. 0 is transparent and 1 is fully opaque. |
<section data-background-video="https://s3.amazonaws.com/static.slid.es/site/homepage/v1/homepage-video-editor.mp4,https://s3.amazonaws.com/static.slid.es/site/homepage/v1/homepage-video-editor.webm" data-background-video-loop data-background-video-muted>
<h2>Video</h2>
</section>Iframe Backgrounds
Embeds a web page as a slide background that covers 100% of the reveal.js width and height. The iframe is in the background layer, behind your slides, and as such it’s not possible to interact with it by default. To make your background interactive, you can add the data-background-interactive attribute.
<section data-background-iframe="https://slides.com" data-background-interactive>
<h2>Iframe</h2>
</section>Background Transitions
Backgrounds transition using a fade animation by default. This can be changed to a linear sliding transition by passing backgroundTransition: 'slide' to the Reveal.initialize() call. Alternatively you can set data-background-transition on any section with a background to override that specific transition.
Parallax Background
If you want to use a parallax scrolling background, set the first two properties below when initializing reveal.js (the other two are optional).
Reveal.initialize({
// Parallax background image
parallaxBackgroundImage: '', // e.g. "https://s3.amazonaws.com/hakim-static/reveal-js/reveal-parallax-1.jpg"
// Parallax background size
parallaxBackgroundSize: '', // CSS syntax, e.g. "2100px 900px" - currently only pixels are supported (don't use % or auto)
// Number of pixels to move the parallax background per slide
// - Calculated automatically unless specified
// - Set to 0 to disable movement along an axis
parallaxBackgroundHorizontal: 200,
parallaxBackgroundVertical: 50
});
Make sure that the background size is much bigger than screen size to allow for some scrolling. View example.
Slide Transitions
The global presentation transition is set using the transition config value. You can override the global transition for a specific slide by using the data-transition attribute:
<section data-transition="zoom">
<h2>This slide will override the presentation transition and zoom!</h2>
</section>
<section data-transition-speed="fast">
<h2>Choose from three transition speeds: default, fast or slow!</h2>
</section>You can also use different in and out transitions for the same slide:
<section data-transition="slide">
The train goes on …
</section>
<section data-transition="slide">
and on …
</section>
<section data-transition="slide-in fade-out">
and stops.
</section>
<section data-transition="fade-in slide-out">
(Passengers entering and leaving)
</section>
<section data-transition="slide">
And it starts again.
</section>You can choose from none, fade, slide, convex, concave and zoom.
Internal links
It’s easy to link between slides. The first example below targets the index of another slide whereas the second targets a slide with an ID attribute (<section id="some-slide">):
<a href="#/2/2">Link</a>
<a href="#/some-slide">Link</a>You can also add relative navigation links, similar to the built in reveal.js controls, by appending one of the following classes on any element. Note that each element is automatically given an enabled class when it’s a valid navigation route based on the current slide.
<a href="#" class="navigate-left">
<a href="#" class="navigate-right">
<a href="#" class="navigate-up">
<a href="#" class="navigate-down">
<a href="#" class="navigate-prev"> <!-- Previous vertical or horizontal slide -->
<a href="#" class="navigate-next"> <!-- Next vertical or horizontal slide -->Fragments
Fragments are used to highlight individual elements on a slide. Every element with the class fragment will be stepped through before moving on to the next slide. Here’s an example: http://revealjs.com/#/fragments
The default fragment style is to start out invisible and fade in. This style can be changed by appending a different class to the fragment:
<section>
<p class="fragment grow">grow</p>
<p class="fragment shrink">shrink</p>
<p class="fragment strike">strike</p>
<p class="fragment fade-out">fade-out</p>
<p class="fragment fade-up">fade-up (also down, left and right!)</p>
<p class="fragment fade-in-then-out">fades in, then out when we move to the next step</p>
<p class="fragment fade-in-then-semi-out">fades in, then obfuscate when we move to the next step</p>
<p class="fragment highlight-current-blue">blue only once</p>
<p class="fragment highlight-red">highlight-red</p>
<p class="fragment highlight-green">highlight-green</p>
<p class="fragment highlight-blue">highlight-blue</p>
</section>Multiple fragments can be applied to the same element sequentially by wrapping it, this will fade in the text on the first step and fade it back out on the second.
<section>
<span class="fragment fade-in">
<span class="fragment fade-out">I'll fade in, then out</span>
</span>
</section>The display order of fragments can be controlled using the data-fragment-index attribute.
<section>
<p class="fragment" data-fragment-index="3">Appears last</p>
<p class="fragment" data-fragment-index="1">Appears first</p>
<p class="fragment" data-fragment-index="2">Appears second</p>
</section>Fragment events
When a slide fragment is either shown or hidden reveal.js will dispatch an event.
Some libraries, like MathJax (see #505), get confused by the initially hidden fragment elements. Often times this can be fixed by calling their update or render function from this callback.
Reveal.addEventListener( 'fragmentshown', function( event ) {
// event.fragment = the fragment DOM element
} );
Reveal.addEventListener( 'fragmenthidden', function( event ) {
// event.fragment = the fragment DOM element
} );
Code Syntax Highlighting
By default, Reveal is configured with highlight.js for code syntax highlighting. To enable syntax highlighting, you’ll have to load the highlight plugin (plugin/highlight/highlight.js) and a highlight.js CSS theme (Reveal comes packaged with the Monokai themes: lib/css/monokai.css).
Reveal.initialize({
// More info https://github.com/hakimel/reveal.js#dependencies
dependencies: [
{ src: 'plugin/highlight/highlight.js', async: true },
]
});
Below is an example with clojure code that will be syntax highlighted. When the data-trim attribute is present, surrounding whitespace is automatically removed. HTML will be escaped by default. To avoid this, for example if you are using <mark> to call out a line of code, add the data-noescape attribute to the <code> element.
<section>
<pre><code data-trim data-noescape>
(def lazy-fib
(concat
[0 1]
<mark>((fn rfib [a b]</mark>
(lazy-cons (+ a b) (rfib b (+ a b)))) 0 1)))
</code></pre>
</section>Line Numbers & Highlights
To enable line numbers, add data-line-numbers to your <code> tags. If you want to highlight specific lines you can provide a comma separated list of line numbers using the same attribute. For example, in the following example lines 4 and 8-11 are highlighted:
<pre><code class="hljs" data-line-numbers="4,8-11">
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>
Click me
</button>
</div>
);
}
</code></pre>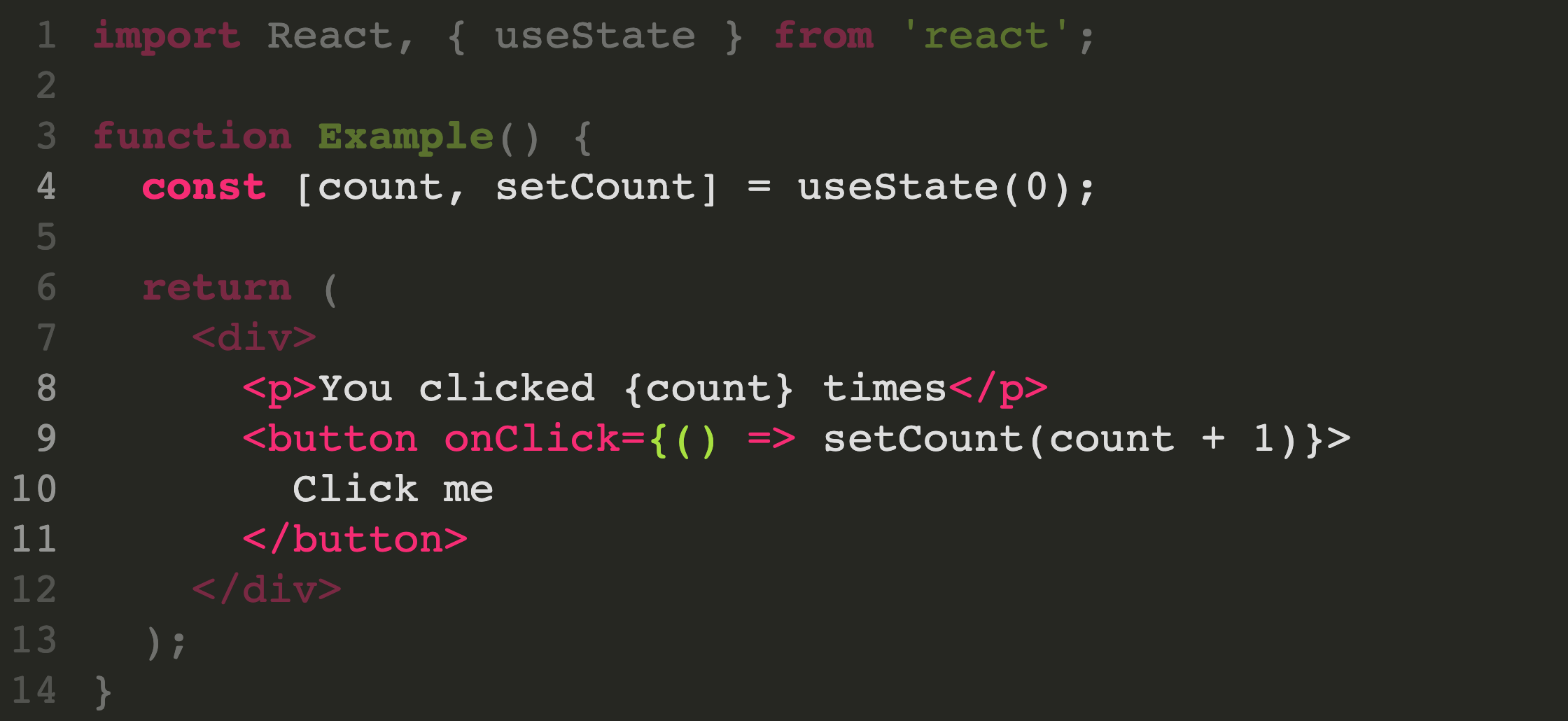
Slide number
If you would like to display the page number of the current slide you can do so using the slideNumber and showSlideNumber configuration values.
// Shows the slide number using default formatting
Reveal.configure({ slideNumber: true });
// Slide number formatting can be configured using these variables:
// "h.v": horizontal . vertical slide number (default)
// "h/v": horizontal / vertical slide number
// "c": flattened slide number
// "c/t": flattened slide number / total slides
Reveal.configure({ slideNumber: 'c/t' });
// You can provide a function to fully customize the number:
Reveal.configure({ slideNumber: function() {
// Ignore numbering of vertical slides
return [ Reveal.getIndices().h ];
}});
// Control which views the slide number displays on using the "showSlideNumber" value:
// "all": show on all views (default)
// "speaker": only show slide numbers on speaker notes view
// "print": only show slide numbers when printing to PDF
Reveal.configure({ showSlideNumber: 'speaker' });
Overview mode
Press »ESC« or »O« keys to toggle the overview mode on and off. While you’re in this mode, you can still navigate between slides, as if you were at 1,000 feet above your presentation. The overview mode comes with a few API hooks:
Reveal.addEventListener( 'overviewshown', function( event ) { /* ... */ } );
Reveal.addEventListener( 'overviewhidden', function( event ) { /* ... */ } );
// Toggle the overview mode programmatically
Reveal.toggleOverview();
Fullscreen mode
Just press »F« on your keyboard to show your presentation in fullscreen mode. Press the »ESC« key to exit fullscreen mode.
Embedded media
Add data-autoplay to your media element if you want it to automatically start playing when the slide is shown:
<video data-autoplay src="http://clips.vorwaerts-gmbh.de/big_buck_bunny.mp4"></video>If you want to enable or disable autoplay globally, for all embedded media, you can use the autoPlayMedia configuration option. If you set this to true ALL media will autoplay regardless of individual data-autoplay attributes. If you initialize with autoPlayMedia: false NO media will autoplay.
Note that embedded HTML5 <video>/<audio> and YouTube/Vimeo iframes are automatically paused when you navigate away from a slide. This can be disabled by decorating your element with a data-ignore attribute.
Embedded iframes
reveal.js automatically pushes two post messages to embedded iframes. slide:start when the slide containing the iframe is made visible and slide:stop when it is hidden.
Stretching elements
Sometimes it’s desirable to have an element, like an image or video, stretch to consume as much space as possible within a given slide. This can be done by adding the .stretch class to an element as seen below:
<section>
<h2>This video will use up the remaining space on the slide</h2>
<video class="stretch" src="http://clips.vorwaerts-gmbh.de/big_buck_bunny.mp4"></video>
</section>Limitations: - Only direct descendants of a slide section can be stretched - Only one descendant per slide section can be stretched
Resize Event
When reveal.js changes the scale of the slides it fires a resize event. You can subscribe to the event to resize your elements accordingly.
Reveal.addEventListener( 'resize', function( event ) {
// event.scale, event.oldScale, event.size
} );
postMessage API
The framework has a built-in postMessage API that can be used when communicating with a presentation inside of another window. Here’s an example showing how you’d make a reveal.js instance in the given window proceed to slide 2:
<window>.postMessage( JSON.stringify({ method: 'slide', args: [ 2 ] }), '*' );
When reveal.js runs inside of an iframe it can optionally bubble all of its events to the parent. Bubbled events are stringified JSON with three fields: namespace, eventName and state. Here’s how you subscribe to them from the parent window:
window.addEventListener( 'message', function( event ) {
var data = JSON.parse( event.data );
if( data.namespace === 'reveal' && data.eventName ==='slidechanged' ) {
// Slide changed, see data.state for slide number
}
} );
This cross-window messaging can be toggled on or off using configuration flags.
Reveal.initialize({
// ...
// Exposes the reveal.js API through window.postMessage
postMessage: true,
// Dispatches all reveal.js events to the parent window through postMessage
postMessageEvents: false
});